When discussing cleaner energy solutions, terms like ‘alternative fuels’ and ‘sustainable’ fuels are often used, sometimes interchangeably. However, while both categories aim to reduce our dependence on traditional fossil fuels, they are not the same.
In this article, we’ll explore the difference between alternative and sustainable fuels and outline what makes each category unique. We’ll also highlight why the distinction between the two is so important.
What are alternative fuels?
According to the UK government, alternative fuels are defined as ‘fuel or power sources which serve, at least partly, as a substitute for fossil oil sources in the energy supply to transport’. This means they support the fight against climate change by reducing our reliance on fossil fuels such as gas, oil and coal.
Examples of alternative fuels include hydrogen, synthetic fuels and biofuels derived from biomass.
What are sustainable fuels?
As a subset of alternative fuels, sustainable fuels also look to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels. However, they must also be produced in ways that can be maintained without depleting resources, harming the environment, or contributing to climate change. They should consider the full lifecycle impact, including emissions, land use, and resource efficiency.
Examples of sustainable fuels include second-generation biofuels (as used in SUSTAIN fuel), hydrogen produced with renewable energy, or synthetic fuels made with green hydrogen and captured CO₂.
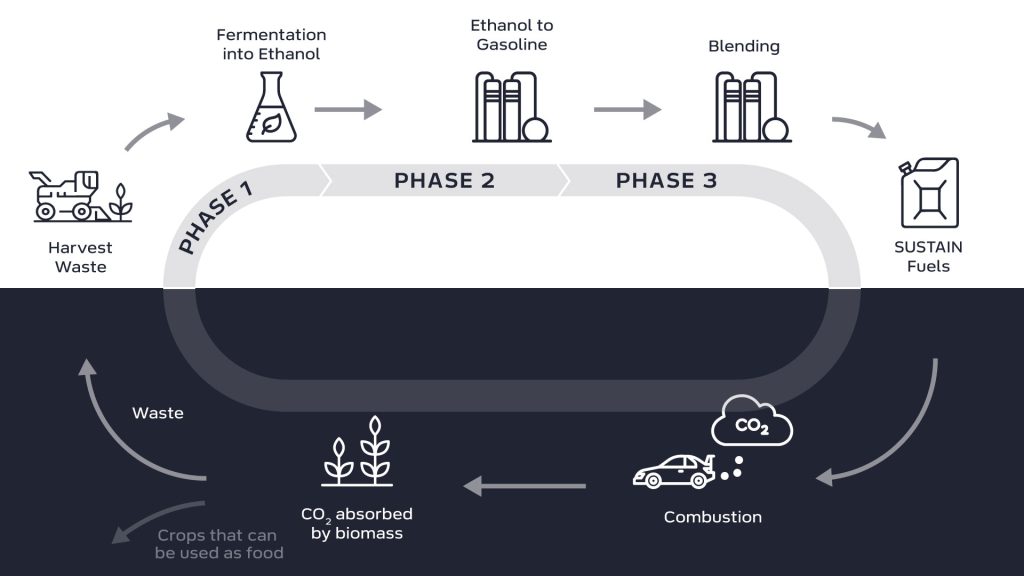
What are the similarities between alternative and sustainable fuels?
Certain similarities between alternative and sustainable fuels lead to the misconception that they are the same.
- The reduction of fossil fuel use: Both categories seek to decrease reliance on traditional fuels, mitigating carbon emissions and pollution.
- They are innovative energy solutions: Both promote research and development of cleaner, more efficient energy technologies.
- They support energy transition: Both play critical roles in transitioning to a lower-carbon economy.
What’s the difference between alternative and sustainable fuels?
Despite these shared characteristics, there are three key differences between alternative and sustainable fuels.
- Resource origin: Alternative fuels can come from both renewable and non-renewable sources, while sustainable fuels are strictly from renewable or eco-friendly sources.
- Environmental impact: Sustainable fuels focus on minimising ecological and carbon footprints, whereas alternative fuels may still have varying environmental impacts.
- Long-term viability: Sustainable fuels are designed for long-term usage without harming the environment, while alternative fuels don’t have to meet this standard.
For example, ethanol from sugarcane that has been grown responsibly may be classed as a sustainable fuel. However, ethanol produced from crops that displace food production or lead to deforestation could only be deemed an alternative fuel.

Why is it important to define between the two categories?
While both alternative and sustainable fuels are vital in reducing our dependence on fossil fuels, sustainable options will ensure that the solution is not just short-term but also ecologically and socially viable in the long run. As the world moves toward a greener future, embracing more sustainable practices will be essential for lasting progress.
As this article explains, whilst all sustainable fuels will be alternative fuels, not every alternative fuel will be sustainable. Knowing the difference between the two categories is key to ensuring we have the right discussions and make the right decisions for our planet in the years ahead. If you’d like to learn more about sustainable fuels or wider fuel categories, please visit the rest of our education hub.